Acute Otitis Media: Symptoms, treatment
Acute Otitis media is a type of inflammation of the middle ear that occurs rapidly, that is, it happens fast. The symptoms start showing up anytime from between a days to 2 week. The commonest symptoms are ear pain and fever. Sometimes, the person may also have drainage of fluid from the ear or even a loss of hearing.
Most of these middle ear infections may not require any treatments, they would go away on their own, whereas, some would require some form of antibiotics.
What is Acute Otitis Media?
Acute Otitis media is a type of inflammation of the middle ear that occurs rapidly, that is, it happens fast. The symptoms start showing up anytime from between a days to 2 week. Other forms of middle ear infection is the Chronic Otitis Media.
What causes Acute Otitis media?
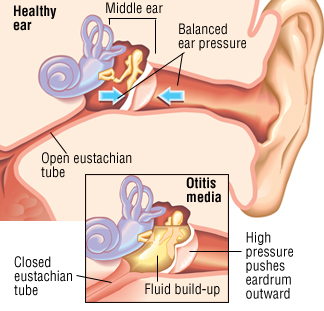
The cause of Acute Otitis Media as well as the simple explanation of the parts of the ear has been discussed previously in our other write up. If you miss that, You can click here to read about otitis media.
Acute Otitis media similarly is mainly caused by migration of organisms from the Throat.
How does this happen?
Infection and inflammation of the middle ear usually happens following an upper respiratory infection such as a common cold. Infections of the upper respiratory tract, may migrate to and lead to swelling of the nasopharynx and the tube that connects it to the ears, the Eustachian tube.
Common organisms that infect the middle ear by migrating from the nasopharynx include mainly bacteria like Streptococcus pneumonia and sometimes Viruses. This process happens more in children because their Eustachian tubes are usually shorter and more horizontal making it easy for fluid to get stuck in them and also because their immune system is not well developed.
The swelling of this tube makes it harder for fluid in the middle ear to drain properly and so it accumulates. The static fluid makes it easy for the bacteria to hang out and multiply
Other causes are: Blockage of the Eustachian tube from force feeding, infections from the blood, and spread from an external ear infection.
What are the Symptoms of Acute Otitis media (AOM)?
For children that are below one year old it might be difficult to diagnose but symptoms that may give a clue, are:
- Ear pain: which may be expressed as Crying and pulling the ears in children who are too young to vocalize
- Fever
- Vomiting and Diarrhea
- General discomfort: Irritability, difficulty feeding, difficulty sleeping.
- Have you ever had water in your ears and it couldn’t come out? That’s how it would feel plus other feelings of illness so it is quite uncomfortable.
- Ear Discharge: There may be a pus like ear discharge if the ear drums have perforated because of build up of pressure behind the ear drum.
- Signs of an upper respiratory tract infection such as cough, a runny nose may also be present
Older children and Adults experience ear pain, hearing loss and a fever.
What to do?
Seeking medical care as soon as these symptoms are noticed is important to prevent complications such as hearing loss, problems with speech and even brain infections.
The earlier you go to the doctor the better for you or your child. You may be referred to an ENT specialist who is a doctor specialized in diseases affecting the ear, nose and throat.
What happens when I get to the hospital?
The doctor would first of all ask some questions about the symptoms and some other details for documentation and to help manage the condition better
After that, the doctor will examine the ears with an otoscope (which is a device that has a light on its end to help doctors have a closer look at the ear drums).
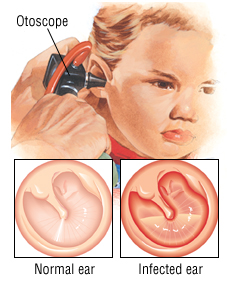
The doctor would observe the ear drum and may see signs of the infection such as redness and bulging.
The doctor may also ask for other tests like a full blood count to help treat the patient better and if there is a discharge, he may also take a sample to culture(grow the bacteria) to figure out the particular bacteria that is causing the infection.
Treatment of Acute Otitis Media (AOM)
Once the doctor has confirmed the diagnosis there are medications that he or she will prescribe to relieve the symptoms of the infection.
- Antibiotics are usually given to clear up the bacteria
- Analgesics (pain medication) and Antipyretics (for the fever)) like Ibuprofen or Paracetamol are usually given for the ear pain and fever.
An affected child may also need to be admitted if less than 3 months or there is a high fever.
What are the complications of Acute Otitis Media (AOM)?
Mastoiditis – Which is the spread of infection to the bone of the middle ear is one of the most important and it causes a painful to touch, red swelling just behind the ear. This can actually spread to the brain so must be treated on admission with Intravenous antibiotics and sometimes, surgery.
Other complications are:
- Chronic Otitis media
- Intracranial abscesses– Collections of pus in the brain,
- Meningitis– Inflammation of the coverings of the brain. See more about Meningitis here.
- Facial Nerve palsy– Damage to a nerve that helps with smiling and raising your brow. That passes through the middle ear.
- Gradenigo syndrome: When the infection involves 2 important nerves, the sixth cranial nerve and the Trigeminal nerve with symptoms of pain behind the eyes and double vision.
What is the outcome?
Generally, the outcome of treatment is great as long as it is treated on time before complications develop.
Feel free to ask any questions you may have by comment below.
Leave a reply
Leave a reply