Dental Carries, Diet, Causes, Prevention, Treatment
Few people are familiar with the term Dental Carries, as it relates to tooth decay. Dental caries, also known as tooth decay, is one of the most common cause of tooth problems in Nigeria and one of the most common reasons for tooth removals.
What is Dental Carries
Dental Caries simply means the decay of the hard tissue components of the teeth and it’s subsequent cavitations.
According to the WHO, Dental caries is the most common noncommunicable disease worldwide
Cause(s) of Dental Carries
Dental Caries is primarily caused by the interaction of bacteria flora in the oral cavity(eg Streptococcus & Lactobacillus species) and dietary sugars(particularly sucrose, glucose and fructose). When we consume a lot of dietary sugars, we provide the substrate that is needed to breakdown our tooth tissue and bring about the decay of our tooth(Dental Cavitations).
Factors that increase the bacteria load of the causative bacteria flora, poor oral hygiene practices, as well as nature of the tooth structure (e.g some people naturally have deep pits and fissures) also play their role in causing Dental Caries, however, increased intake of refined sugars is the most effective cause of tooth decay.
Symptoms of Dental Carries
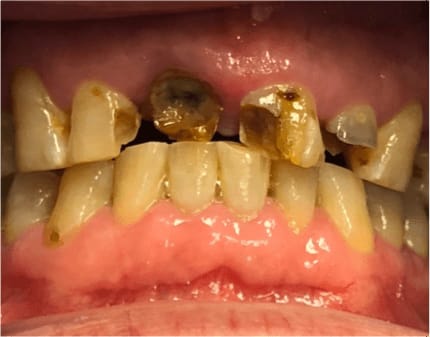
Presence of Dental Caries maybe difficult to detect at the onset, due to the hardness of outermost structure of the tooth(ie the enamel, which is the hardest tissue of the human body, before bones). Hence symptoms of Dental Caries may present in the following progression;
– dark brown discolouration of the tooth surface
– sensitivity of the tooth to hot or cold substances
– hole(s) in the tooth which may or may not be association with entrapment of food particles
– pain on chewing or even without stimulation.

Treatment of dental Carries
This usually depends on the extent of the carious lesion.
1) A carious lesion that has not progressed significantly may be arrested by improvement in oral hygiene practices and/use of fluoride therapies.
2) A hole in the tooth can be covered up by the use of dental filling materials at the restorative dental unit
3) A carious tooth may be treated by Root Canal Therapy, according to the clinician’s discretion and patient’s affordability.
4) Extraction may become the treatment option in a case of badly damaged or unrestorable tooth.
Prevention of Dental Carries
- The need for routine dental visits is key to the maintenance of oral health. Routine scaling and polishing during such visits is highly recommended, with an interval of atleast six months preferabe. This could be regarded as a prophylactic measure since your regular tooth brushing is never sufficient to eliminate food particles from the mouth.
- The use of dental floss for the removal of food particles and strands lodged between teeth surfaces(inter proximal surfaces of teeth). This should be used to replace the use of tooth picks as they are safer and less traumatic.
- Regular rinsing of the mouth following the consumption of sugar rich dry and sticky foods such as chocolates, cakes, breads, biscuits as well as foods with significantly high hidden sugars eg baked beans, breakfast cereals, tomato ketchup etc.
- Modification of intake of sweetened drinks and carbonated drinks.
- Reduction of overall amount of sugary food intake by checking the manufacturer’s labels and avoiding foods with sugars such as sucrose, glucose and fructose listed in the ingredients. It should be noted also that natural sugars (eg honey, brown sugars) have as much caries risk as purified or added sugars.
However, when sweetened foods are required, choose those containing sweetening agents such as saccharin, acesulfame-K and aspartame. These diet formulations contain less sugar than their standard counterparts.
Generally, we should become accustomed to a less sweet diet!
Feel free to ask any questions you have below, and I would do my best to answer you as soon as I can.
Leave a reply
Leave a reply