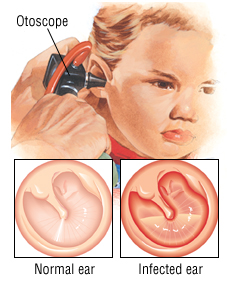
Otitis Media (Middle Ear Infection): Causes, Symptoms
Otitis is just a fancy term that means inflammation or swelling of the ear. When this swelling affects the middle ear, it is called otitis media. For the sake of clarification, The ear has 3 parts (external, middle and inner) which can all be inflamed and infected. If it affects the external part of the ear, that is the part that you can see, we call it Otitis Externa.
Children are more prone to these middle ear infections than adults. Most times, this middle ear infections clear up on their own, and you would not need any treatment except those given to manage the pain.
What is Otitis Media?
Otitis media is a disease of the middle ear that causes it to become inflammed or swollen. The two common types that we know are the acute otitis media (AOM) (happening suddenly) and the chronic otitis media (COM) (happening over a longer period of time). Otitis media usually causes ear pain. In children, this can cause increased crying and poor sleep.
Acute otitis media (AOM) is very common in children with most children (75%) having at least one episode before they are 3 years old and so this is a very important topic for mothers to acquaint themselves with to be able to recognize and prevent the harmful complication.
Where is the middle ear?
To help us understand better, Let’s take a brief look at the different parts of the ear
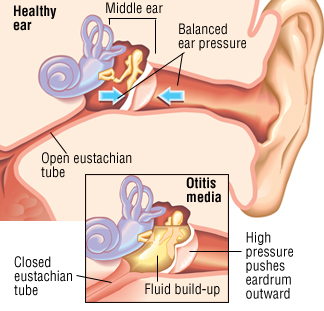
1. The External Ear is made up of the Pinna (the part of the ear that you can see and touch) and the external auditory meatus which is a small tube connecting the Pinna to the eardrum.
2. The Middle ear is a small bony chamber that lies behind our ear drums and contains three little bones called ossicles which help transmit vibrations to our inner ear. The Eustachian tube is a short tube that connects the nasopharynx which is the back of the nose and throat, to the middle ear and is super important to the topic because that is the main source of the infection!
The Eustachian tube helps to:
- Adjust the pressure in the middle ear.
- Protect the middle ear from secretions from the nasopharynx
- Drain secretions from the middle ear to the nasopharynx.
To help you understand better, it is what pops open when you yawn.
3. The Inner ear takes the vibrations from the middle ear and converts them into nerve impulses that can be interpreted by our brains as sound.
Types of Otitis Media
- Acute Otitis Media
- Otitis media with effusion
- Chronic otitis media with effusion
- Chronic suppurative otitis media
Causes of Otitis Media (Middle Ear Infection)
The infection of the middle ear is commonly caused by a virus or a bacterium that entered the ear. Sometimes, it can be as a result of infection from other part of the body such as the congestion and swelling of the nose, throat and eustachian tubes, as seen in a cold, flu or allergy. The bacteria or viral agent can get into the ear from these places through the Eustachian tube.
Symptoms of Otitis Media (Middle Ear Infection)
The of signs and symptoms of otitis media are different depending on if the person is an adult or a child.
common Signs and symptoms in children include:
- Ear pain
- Trouble sleeping
- Incessant crying
- Tugging or pulling the ear
- Drainage of fluid from the ear
- Fever
- Difficulty in hearing or responding to calls
- Headache
Signs and symptoms common in Adult include:
- Ear pain
- Trouble hearing
- Drainage of fluid from the ear
Risk factors for Otitis Media (Middle Ear Infection)
Risk factors for middle ear infections are:
- Age: The infection of the middle ear is more common among children between the ages of 6 months and 2 years. This is partly due to the immaturity of their immune systems, as well as the size and shape of their Eustachian tube.
- Children in Day care centres: These children in daycare centres are more exposed to infections, such as, Conjunctivitis, common cold, etc than those who are at home.
- Bottle Feeding Babies: Babies are fed from a bottle, tend to have more of these middle ear infections than those who were. Breast milk also help in building the child’s immunity and helping the baby fight against these infections.
- Smoke and Pollution: Exposure to tobacco smoke in any form as well as high levels of air pollution can increase the chances of developing these middle ear infections.
Treatment of Otitis Media
If your child has any infection of the middle Ear, you should take him or her to the doctor (particularly, an Ear, Nose and Throat specialist also known as an Otolaryngologist). He will examine your child and give you the necessary medications for the infection.

Please, do not abuse antibiotics especially with children. Remember that children are more prone to dangers from drugs due to their small size.
Prevention of Otitis Media
The following strategies can help to reduce your risk of developing ear infections:
- Prevent common colds and other illnesses.
- Avoid smoking or exposing your child to smokes.
- Breast-feed your baby exclusively. That is, you should breast-feed your baby for at least six months.
- Vaccinations: at the appropriate time can help prevent ear infections from organisms like pneumococcus and other bacterial infections.
Feel free to ask any questions you may have about this condition below.
Leave a reply
Leave a reply